Retina
An emergency situation known as retinal detachment occurs when the retina separates from the choroid, the central layer of the eye (middle layer of eye)
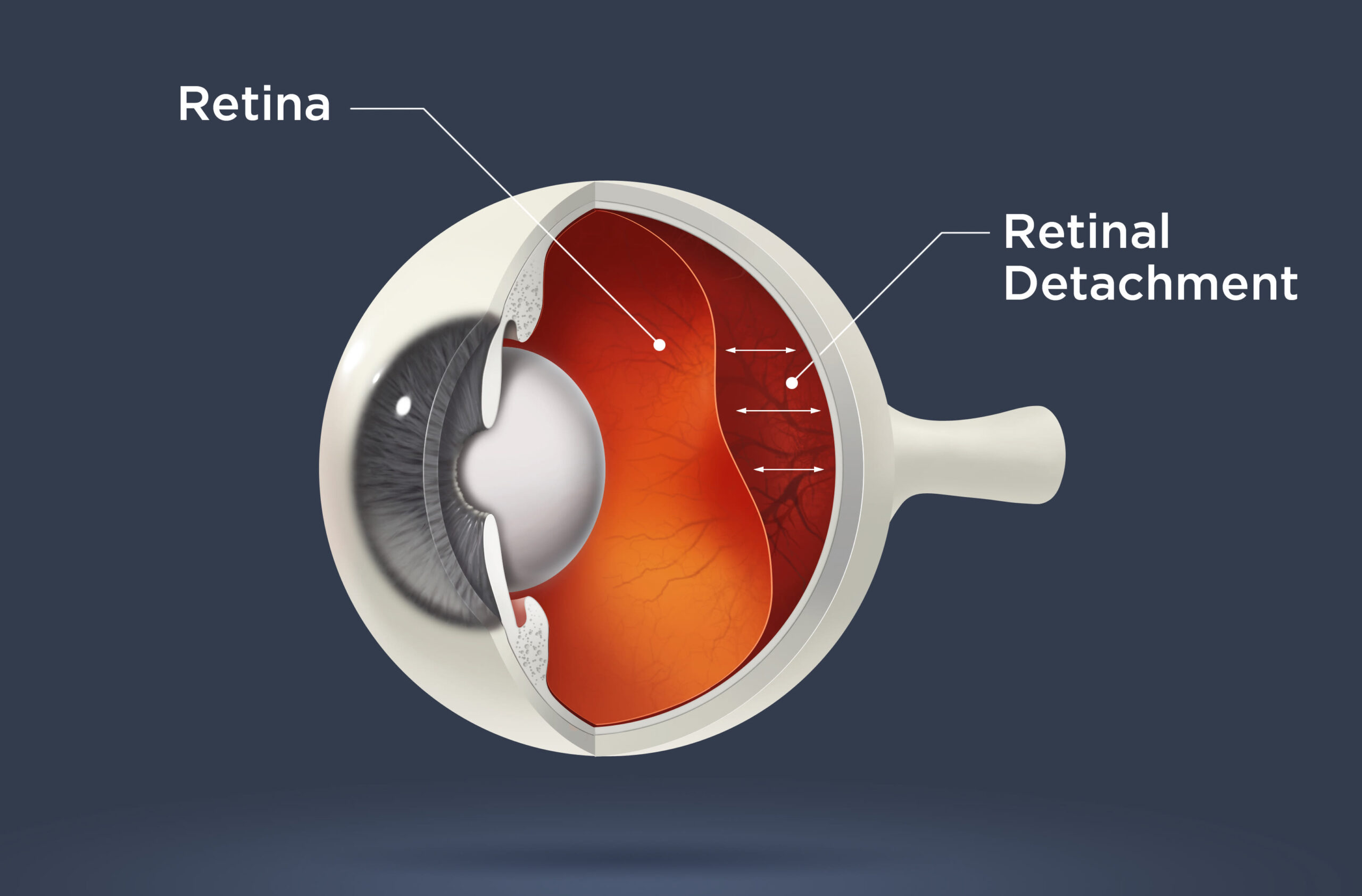
Retina
What is Retina?
Retina: Located near the optic nerve, the retina is a thin layer of tissue which overlays the back of the eye from the inside. The prime purpose of the retina is to receive light which is focused on the lens, then convert the light in neural signals, and then send these signals on to the brain for visual recognition.
As retina plays a vital role in vision, damage to it can cause permanent loss of vision. Ailments such as Retinal Detachment, in which the retina is unexpectedly detached from its natural place, can restrict the retina from accepting and processing light. Thus preventing the brain from obtaining this information and leading to blindness.
When the retina gets separated from the nerve tissues and also the blood supply underneath it, Retinal Detachment occurs. Retinal detachment can be treated but it must be taken care of very effectively otherwise in worst cases, it can lead to permanent loss of vision. Retinal detachment is a painless condition but it is usually seen having clouding effect like a grey curtain moving in front of eyes.
A retina specialist can figure out retinal detachment by doing some retinal and pupil response tests. These tests start from initial and simple visual acuity testing to advanced level ultrasound of the eye. The patient of retinal detachment starts getting the grey curtain in the vision at the inception stages of detachment process. Before the case gets worse, some symptoms and signs can be looked into to understand the beginning of retinal detachment.
Retina symptoms include:
Sudden decrease in vision.
Increase in the number and size of eye floaters.
Floaters with flashes.
Shadows in peripheral vision
If you are facing any of the above mentioned, it is always safe to see a doctor in order to prevent further complications. Retinal Detachment should not be ignored. Severe cases of Retinal Detachment can lead to permanent loss of vision.
What Causes Retinal Detachment?
The retina is connected to the vitreous, clear gel in the center of the eye. As our age increases, the vitreous may contract and sometimes while the process of the vitreous shrinking it might remain partially attached to the retina, and tug on it. This results in displacement of the retina’s nerve cells causing eye flashes.
Usually, this doesn’t cause any issues, but in some cases, it can tug enough to tear the retina allowing eye fluid to enter it. As fluid goes inside, it exerts pressure on the retina pushing it away from the tissue beneath, creating division, and ultimately, detachment.
Injury can also cause retinal detachment. Blunt trauma and some eye ailments like advanced diabetic eye condition and critical myopia.
The portion of the retina which is detached can no longer transmit light signals to the brain properly. Vision also gets disrupted by retinal blood vessels that leak fluid into the inner portion of the eye where vitreous, or gel-like like fluid would typically be. If the retinal detachment advances into the macula which is the central part of the retina, the result on vision becomes more critical.
Treatment of Retinal Detachment?
A proper retina treatment is necessary for retinal detachment. Retinal surgery is a proven and safest treatment for retinal detachment. It is also important to take the right a retina treatment as when it is detected. To ensure that retina treatment is effective, the patient should be treated with 24 hours in order to avoid the case going out of hands.
Retina treatment procedures include the following things:
Laser Surgery: Laser surgery repairs the tears in the retina which is the primary cause of detachment.
Cryopexy: Cryopexy is the application of intense cold to underlying tissue which will cause scaring resulting in holding the retina intact in that place.
Pneumatic Retinopexy: This procedure uses a tiny gas bubble which is placed inside the eye which brings the retina back in its place. It is generally followed by laser surgery to assure that the retina stays in the right place permanently.
• Scleral Buckle: Scleral buckle: It is the suturing of a silicone “buckle” into the eye which orders the wall of the eye into a place that admits the retina to reattach.
Don’t worry you are in safe hands. If you observe any slightest symptoms of this eye problem, please see the doctor as soon as possible. It may cost your eye sight if ignored.
